Context
Initial Problem Space
The project began with a focus on designing and prototyping interactive experiences for use in homes, leveraging Artificial Intelligence (AI). As interaction designers, our task was to map out new kinds of interactions enabled by the increasing prevalence of AI technology in domestic environments.
The way we interact with digital products and services continues to diversify beyond traditional methods: keyboard, mouse, touch, and screens. It is now possible to control your TV with a wave of your hand, order dinner by speaking to a glowing box on your kitchen counter, and visit far-off places from your couch just by wearing a headset.
AI in the home also holds the potential for significant quality-of-life improvements for individuals with various conditions impacting their mobility and independence. For instance, AI can help older adults stay in their homes longer and support those with mental health issues in becoming more independent. These advancements depend not only on the power of AI algorithms to process and understand data but also on how these algorithms are embedded into interfaces that people can interact with.
Project Genesis
Habitracker was conceived to address the specific needs of users suffering from atopic diseases. The goal was to create an AI-driven habit monitor that guides users in positively changing their behaviour and actions to prevent their condition from worsening and to enhance their overall quality of life. The design was inspired by the potential of AI to offer significant quality-of-life improvements through intelligent, interactive interfaces.
Research and Ideation
Initial Research and Concept Development
To ensure Habitracker addressed the specific needs of users managing atopic diseases effectively, we formulated overarching research questions aimed at gaining comprehensive insights into 'Healthcare at home.'
Research Questions:
1. How does the user feel about the current state of their household’s health?
2. What are the user’s largest concerns regarding their health?
3. What are the common sicknesses and current disease prevention measures taken within the home?
4. What products/services are most often used to maintain home hygiene?
5. What technologies are used in the home to manage healthcare?
1. How does the user feel about the current state of their household’s health?
2. What are the user’s largest concerns regarding their health?
3. What are the common sicknesses and current disease prevention measures taken within the home?
4. What products/services are most often used to maintain home hygiene?
5. What technologies are used in the home to manage healthcare?
Exploratory (Secondary) Research
Preventative Health:
Effective strategies for promoting wellness and preventing diseases include managing risk factors such as physical inactivity, high blood pressure, and cholesterol. These factors contribute significantly to Australia's burden of disease, accounting for 32% of the total. Additionally, maintaining clean home environments through activities like thorough dusting can improve air quality and reduce risks of allergies and asthma.
Effective strategies for promoting wellness and preventing diseases include managing risk factors such as physical inactivity, high blood pressure, and cholesterol. These factors contribute significantly to Australia's burden of disease, accounting for 32% of the total. Additionally, maintaining clean home environments through activities like thorough dusting can improve air quality and reduce risks of allergies and asthma.
Medication Management:
Adherence to medication is critical yet challenging, with statistics showing that 30-50% of people do not take medications as prescribed. This non-adherence leads to significant impacts, including 12% of medical admissions and higher rates among older adults. Innovations like Telesofia Medical's video communication platform aim to simplify medication instructions, ensuring better compliance and health outcomes.
Adherence to medication is critical yet challenging, with statistics showing that 30-50% of people do not take medications as prescribed. This non-adherence leads to significant impacts, including 12% of medical admissions and higher rates among older adults. Innovations like Telesofia Medical's video communication platform aim to simplify medication instructions, ensuring better compliance and health outcomes.
Medication Management:
Home-based health monitoring systems, such as Medibank's sensor technology, offer promising avenues for improving patient outcomes. These systems track movement and temperature, providing real-time health data analysis. Research indicates that home care interventions can lead to a 20% lower mortality rate and reduce healthcare costs compared to hospital stays. Fitbit, originally a fitness-tracking device, has expanded into healthcare by integrating data on activity, exercise, nutrition, and sleep to support disease management and wellness programs.
Home-based health monitoring systems, such as Medibank's sensor technology, offer promising avenues for improving patient outcomes. These systems track movement and temperature, providing real-time health data analysis. Research indicates that home care interventions can lead to a 20% lower mortality rate and reduce healthcare costs compared to hospital stays. Fitbit, originally a fitness-tracking device, has expanded into healthcare by integrating data on activity, exercise, nutrition, and sleep to support disease management and wellness programs.
Analysing articles and papers to understand existing technologies and insights relevant to home healthcare. These insights highlight ongoing advancements and strategies in home healthcare, emphasising the importance of preventative measures, effective medication management, and innovative health monitoring solutions
Interview (Semi-Structured)
To gain a deeper understanding of the individual experiences and perspectives of potential users, I conducted semi-structured interviews with five participants. These interviews were designed to be flexible, allowing for both prepared and spontaneous questions to capture a comprehensive view of the participants' lives, circumstances, and decision-making processes. The prepared questions focused on their health concerns, current household health management practices, and their experiences with existing health-related technologies. Throughout the interviews, additional questions were asked to clarify and expand on topics as they arose, ensuring a thorough exploration of each participant's unique situation. This method provided rich qualitative data that informed the design process, revealing common themes and individual nuances that shaped the final concept.
Contextual Inquiry
In addition to the interviews, contextual inquiries were conducted with five participants to observe and understand their interactions within their personal environments. This method involved spending time with participants in their homes, observing their daily routines, and asking questions about their health management practices. By capturing the user in their natural setting, I was able to gain insights into their habits, the tools they used, and the social, technical, and physical environments that influenced their behaviour. Key findings from these inquiries included the identification of pain points in their current health management routines, the discovery of unspoken needs, and a deeper understanding of how their environment impacted their health and wellbeing. These observations were crucial in designing a solution that was not only effective but also seamlessly integrated into the users' daily lives.
Design and Prototyping
Sketches
We began the design process with extensive sketching, jotting down all sorts of ideas and plans for the concept. This stage was crucial for brainstorming and exploring different approaches to the problem. Initial sketches included rough layouts of how the user would interact with our AI solution and various features that could be incorporated. As we refined the details, these sketches evolved into more structured wireframes. Sketching allowed us to visualise the user journey and interface design early on, making it easier to identify potential issues and iterate quickly. This iterative process helped in forming a clear and cohesive vision for the final product.
As part of the design conceptualisation process, two idea concepts were created:
Concept 1: A system that focused on helping users create and maintain good hygiene and health habits, which will prevent or soothe atopic diseases in the home
Concept 2: A system which helps users identify foods that cause atopic disease flareups, and overtime help users to understand and predict their dietary triggers.


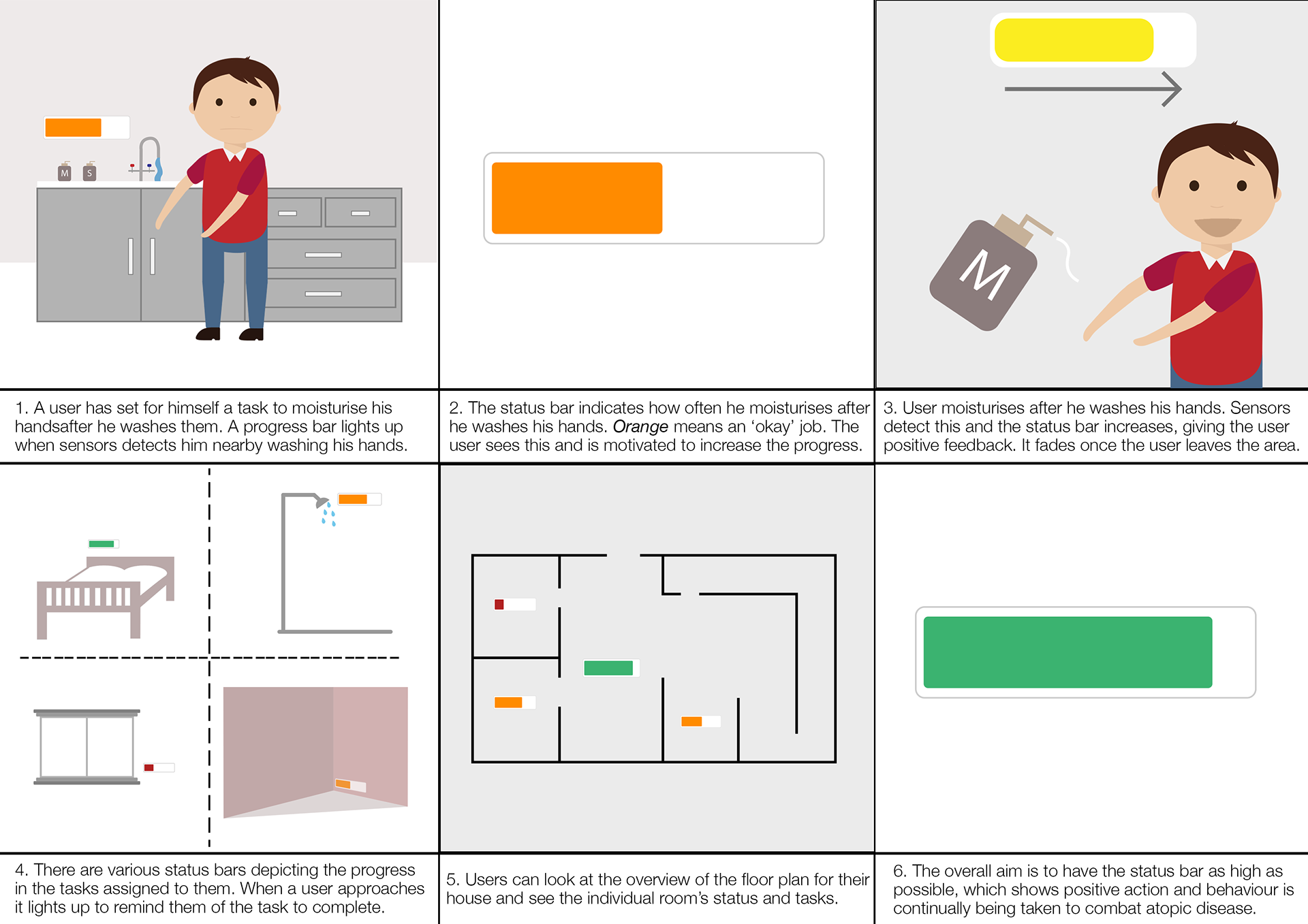
Storyboarding and User Journey Map
Following the sketches, we created detailed storyboards to visualise how users would interact with Habitracker in various scenarios. These storyboards mapped out the entire user journey, from initial setup and daily interactions to long-term use and troubleshooting. This helped us identify potential pain points and opportunities for enhancing user experience. Additionally, we developed a user journey map to illustrate the steps users would take to achieve their goals, highlighting touchpoints and interactions with the AI system. These devices was based on the persona developed from all the UX research gathered.
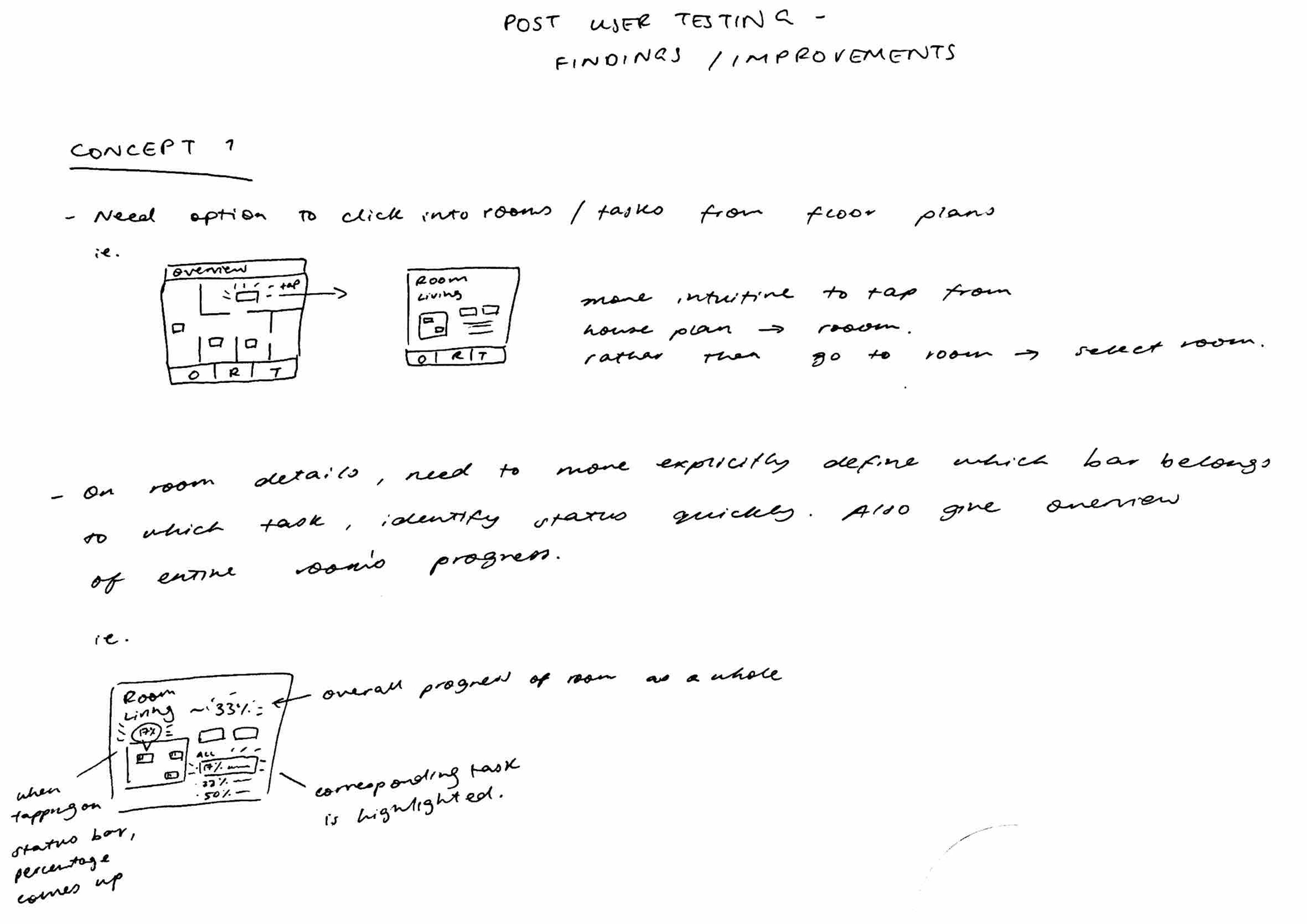
User Testing and Findings
User Testing Sessions
We conducted user testing sessions with five participants for both concepts developed during the prototyping phase. Each session involved guiding users through our prototypes using a set of predefined tasks, while employing the concurrent think-aloud method to capture real-time feedback. After completing the tasks, participants provided retrospective thoughts on their experience.
Overall Comments
Feedback from user testing highlighted several key points for both concepts:
• Both concepts were deemed useful and beneficial for individuals managing atopic diseases at home.
• Concept 1 was perceived as a more holistic solution, capturing a broader scope of potential triggers. However, participants noted that the interface needed improvement in terms of intuitiveness.
• Concept 2 received praise for its idea of matching food choices with potential health effects, allowing users to identify problematic foods. Participants suggested that earlier feedback on food choices would enhance its usability.
Findings and Justification
Findings and Justification
Based on the user testing sessions and feedback received, Concept 1 - the Good Habits Monitor emerged as the preferred solution to move forward with. This decision was justified for several reasons:
• Target Specificity: Concept 1 effectively targets the specific needs of individuals with atopic diseases.
• User Interaction: It provides a greater focus on interacting with users, enhancing engagement and usability.
• Integration: The concept seamlessly integrates into the home environment, supporting a comprehensive approach to health management.
• Flexibility: It offers greater flexibility in adapting to diverse user needs and preferences.
• Accuracy: Concept 1 demonstrated higher accuracy in monitoring and addressing health-related habits and triggers.
By selecting Concept 1, we aim to advance a solution that not only meets the functional requirements of managing atopic diseases but also enhances user experience through intuitive design and comprehensive functionality.
By selecting Concept 1, we aim to advance a solution that not only meets the functional requirements of managing atopic diseases but also enhances user experience through intuitive design and comprehensive functionality.
ITERATIONS
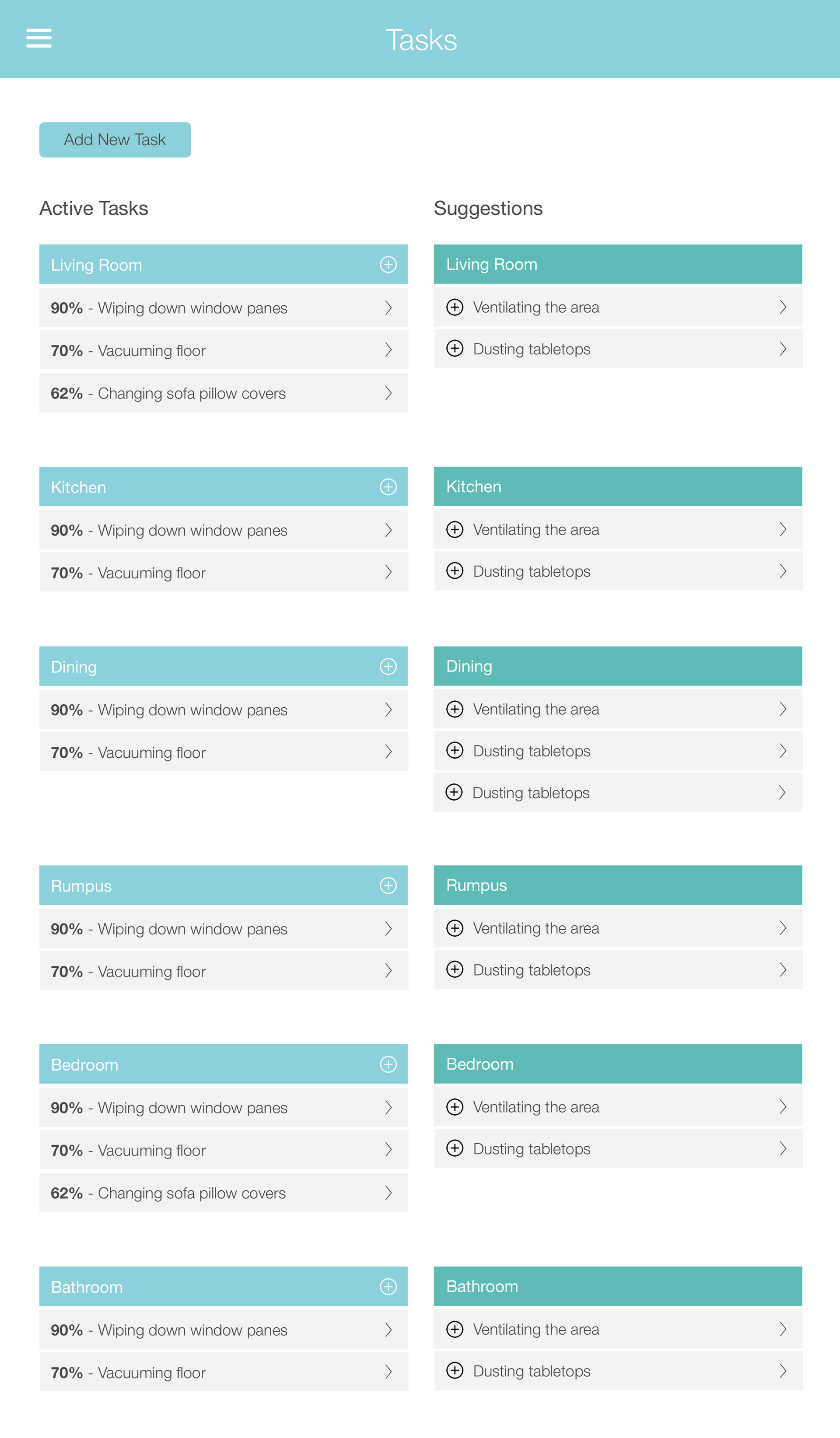
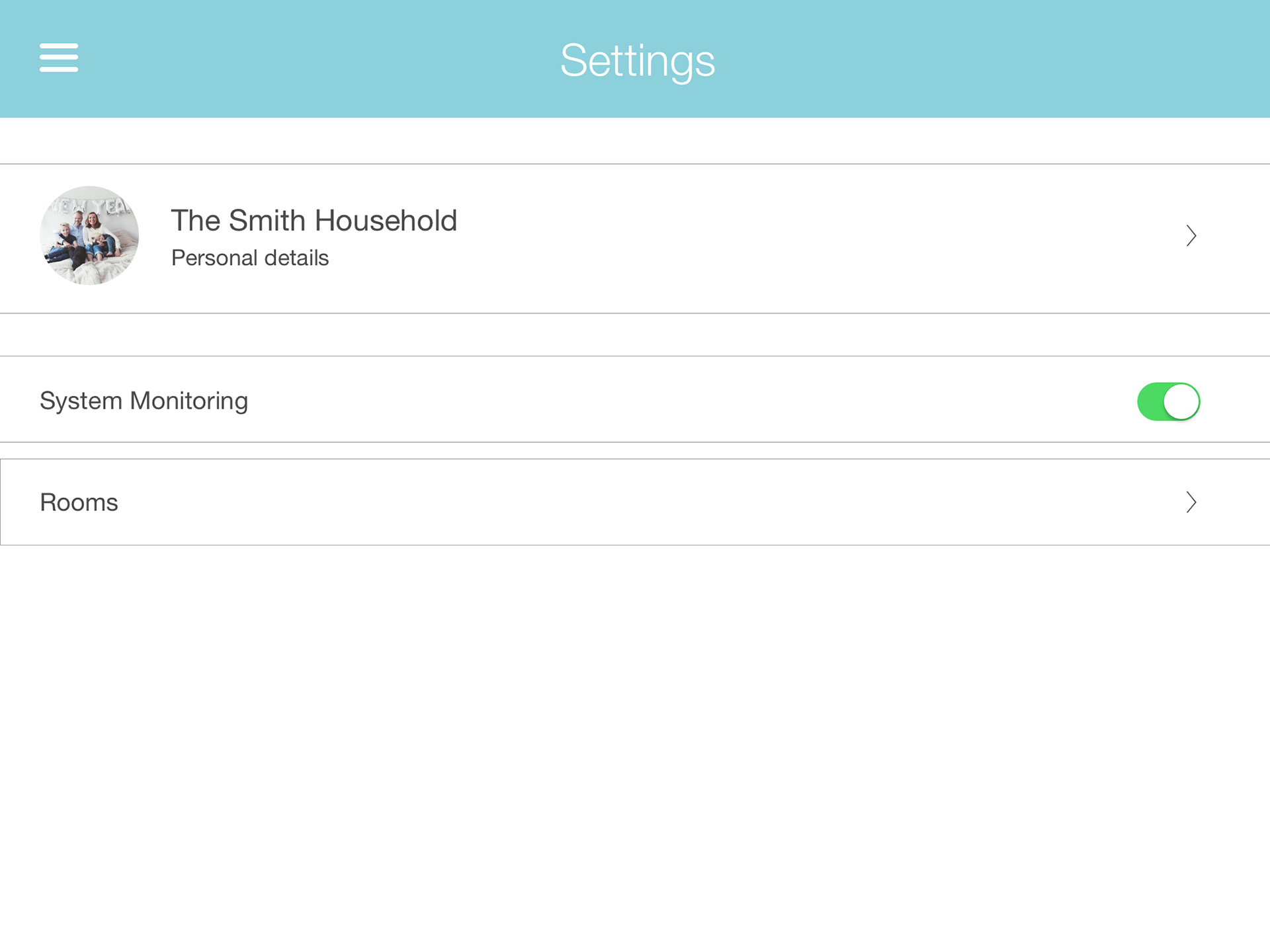
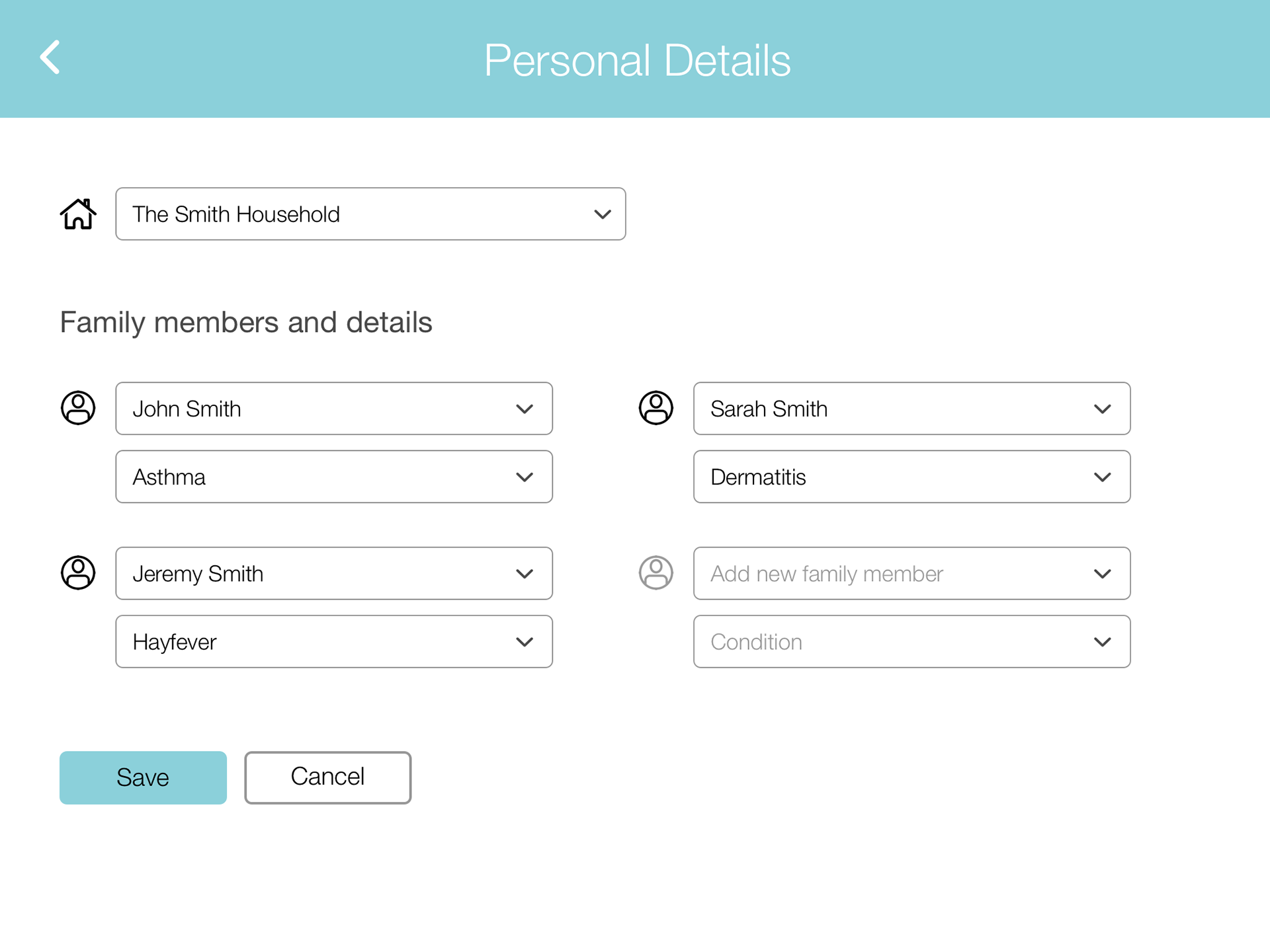
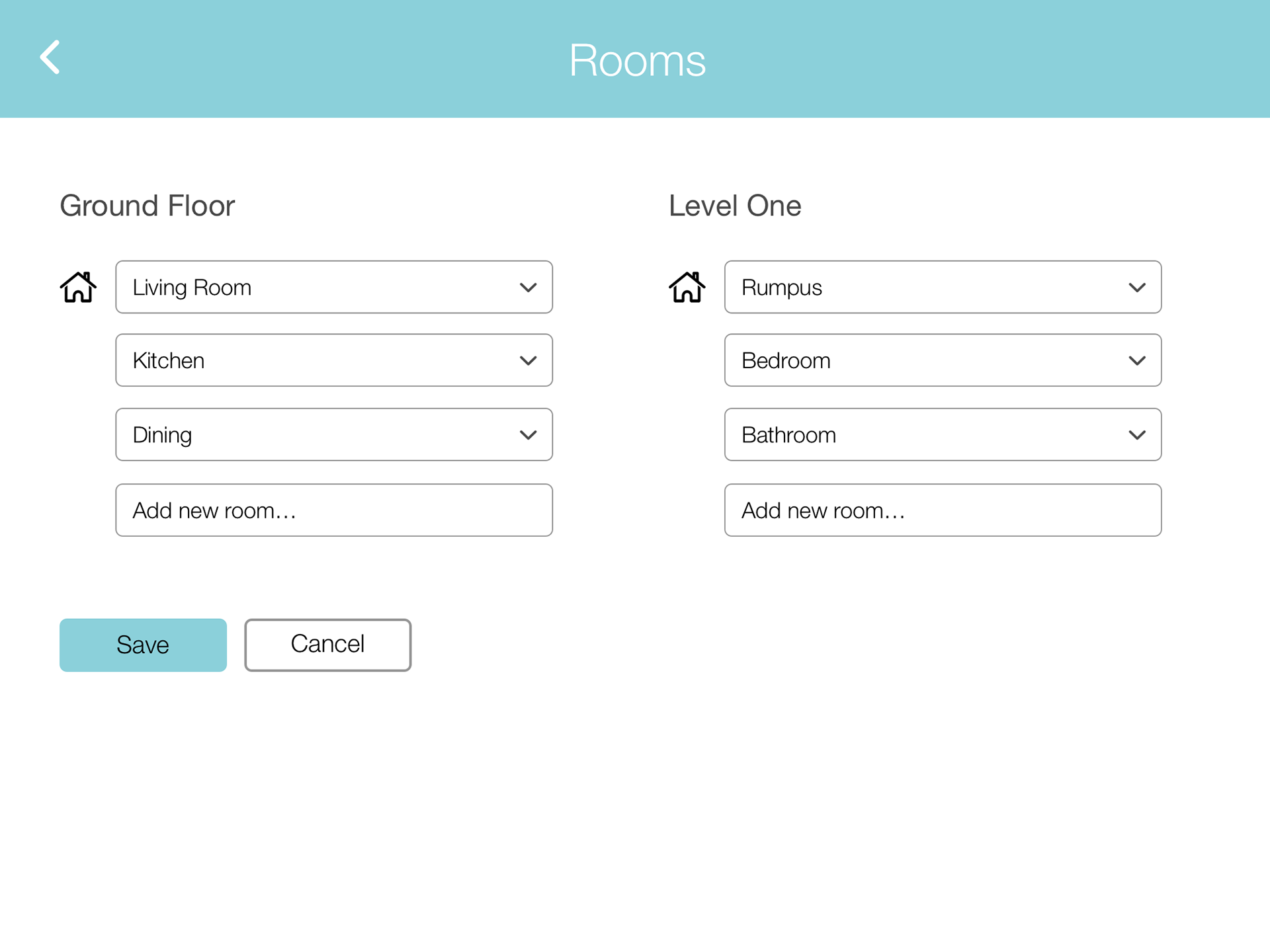
The rough sketches were transformed into wireframes, which went through multiple iterations based on feedback and further ideation. This iterative process ensured that the design was continuously improved and aligned with user needs.
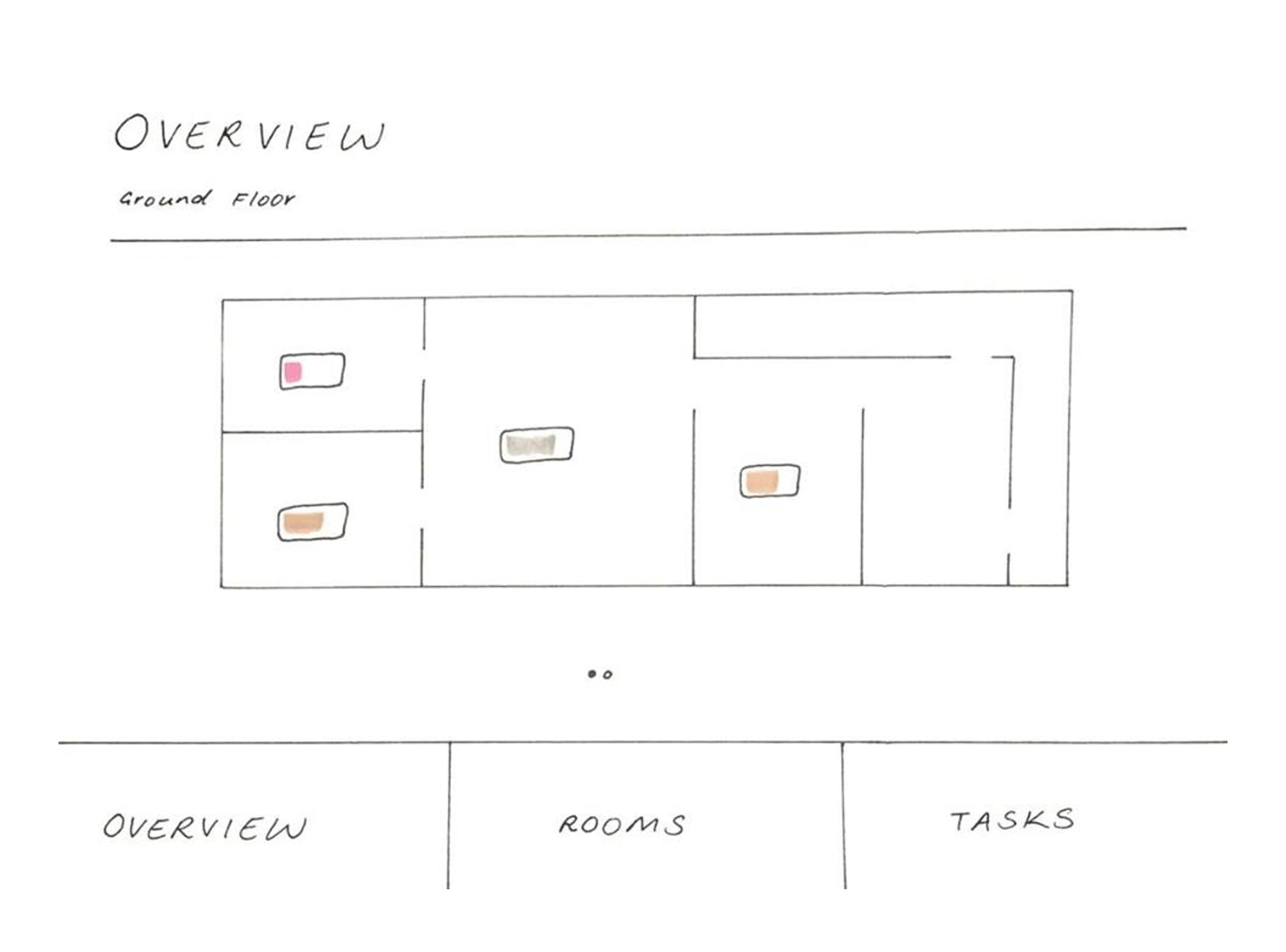
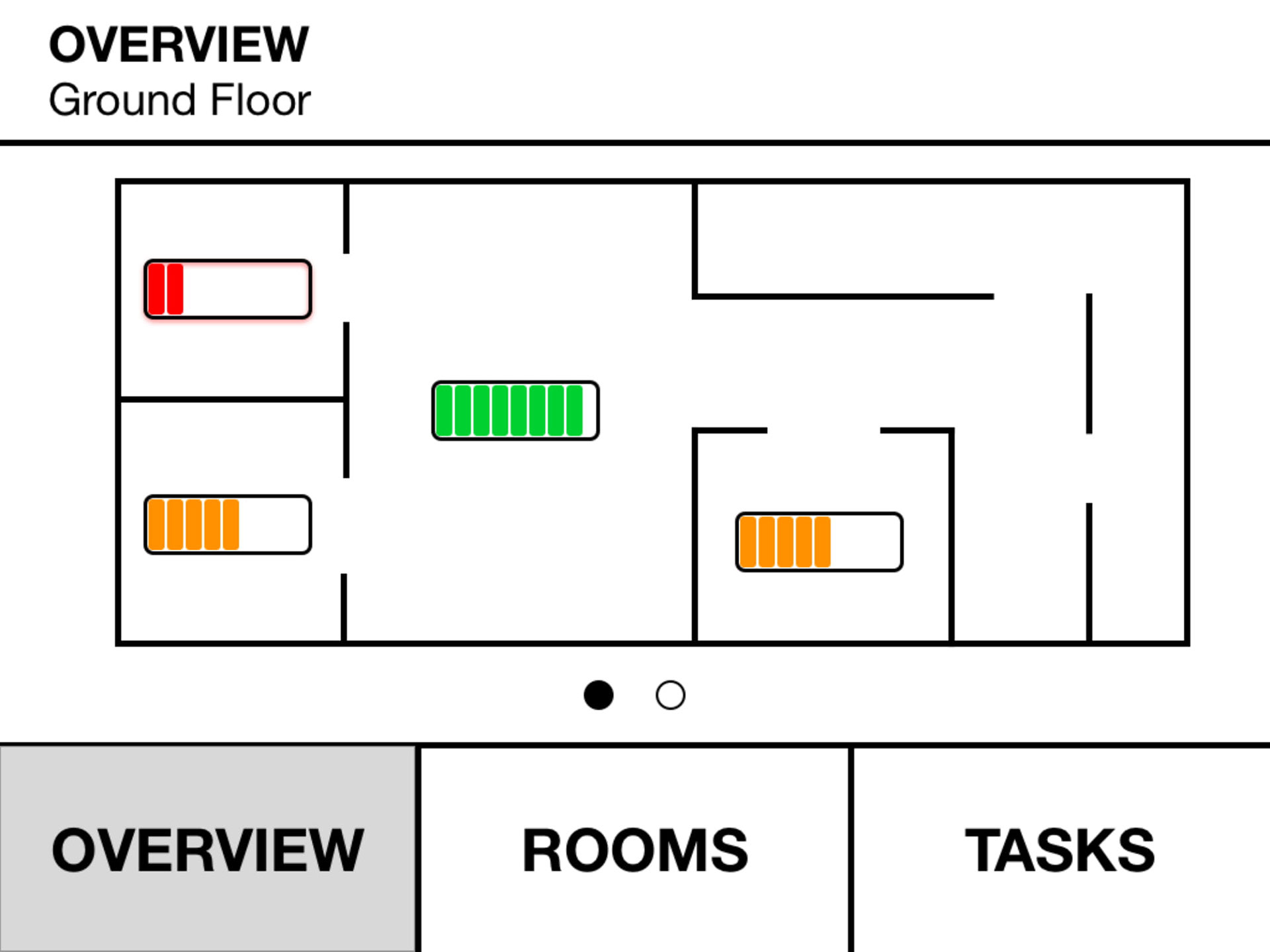
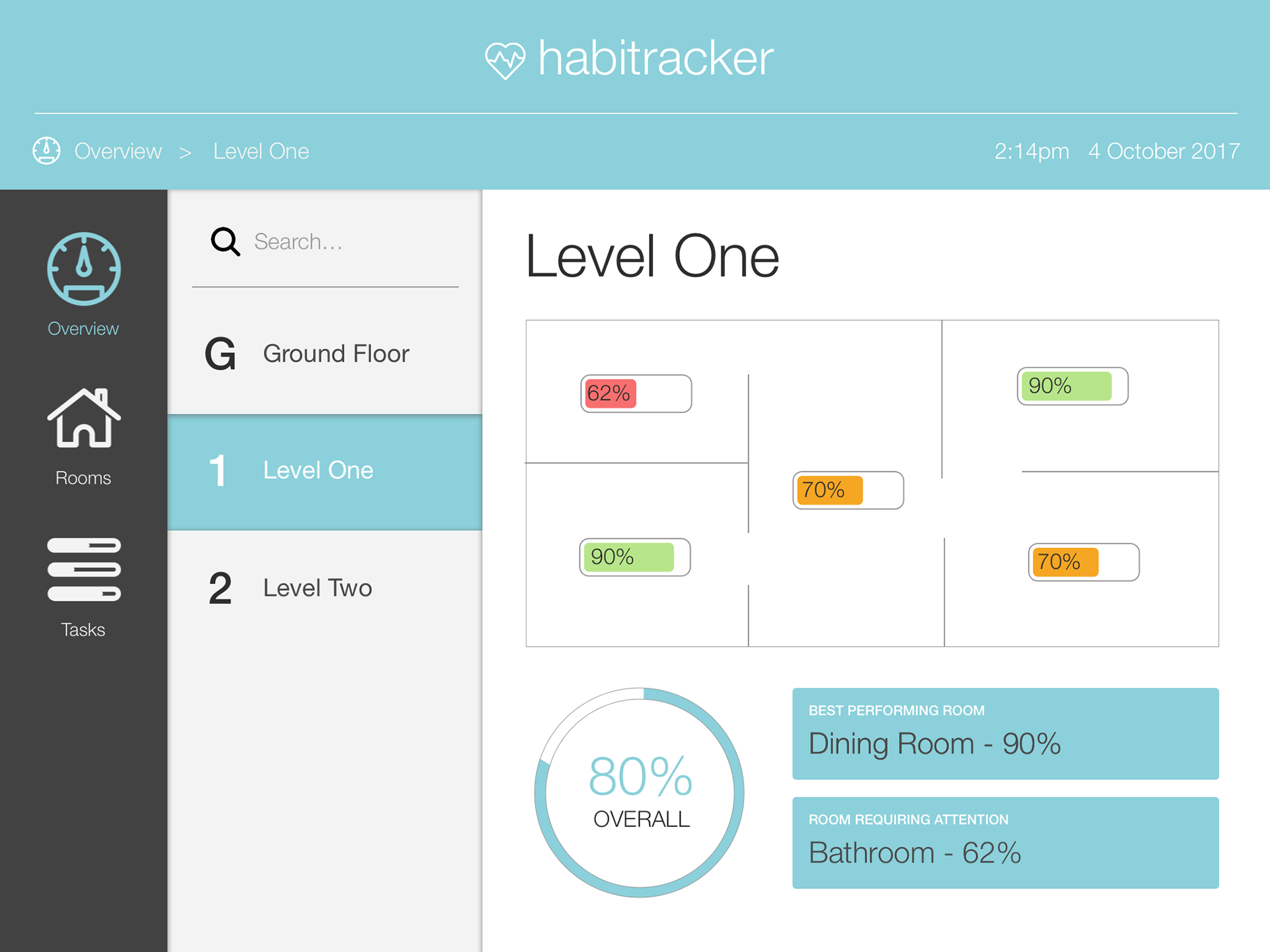
Final Solution
The final design was a result of comprehensive research, iterative design, and user feedback. It effectively addressed the needs of atopic disease sufferers, providing them with a tool to manage, improve, and prevent the worsening of their condition, thereby enhancing their quality of life.

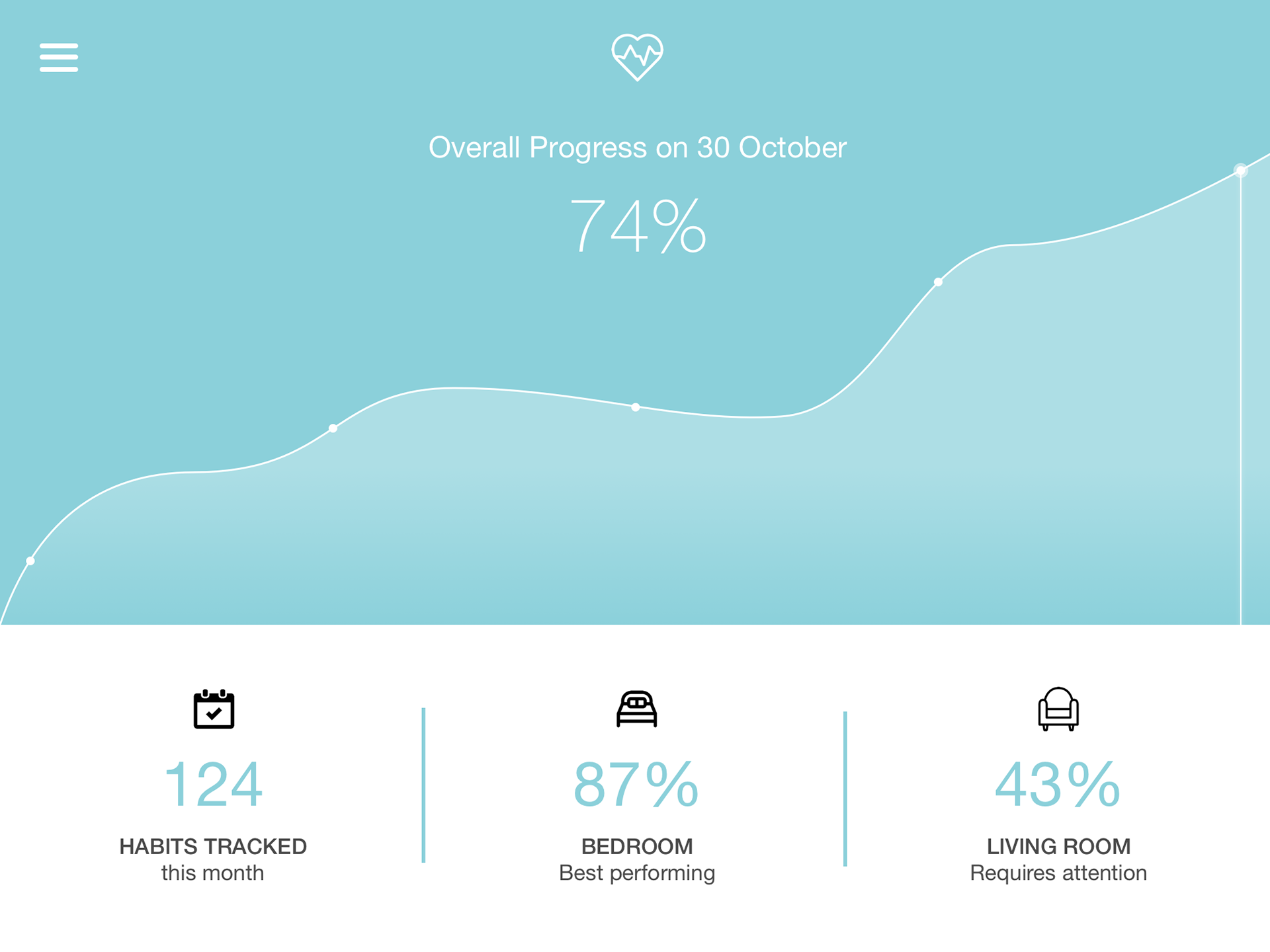
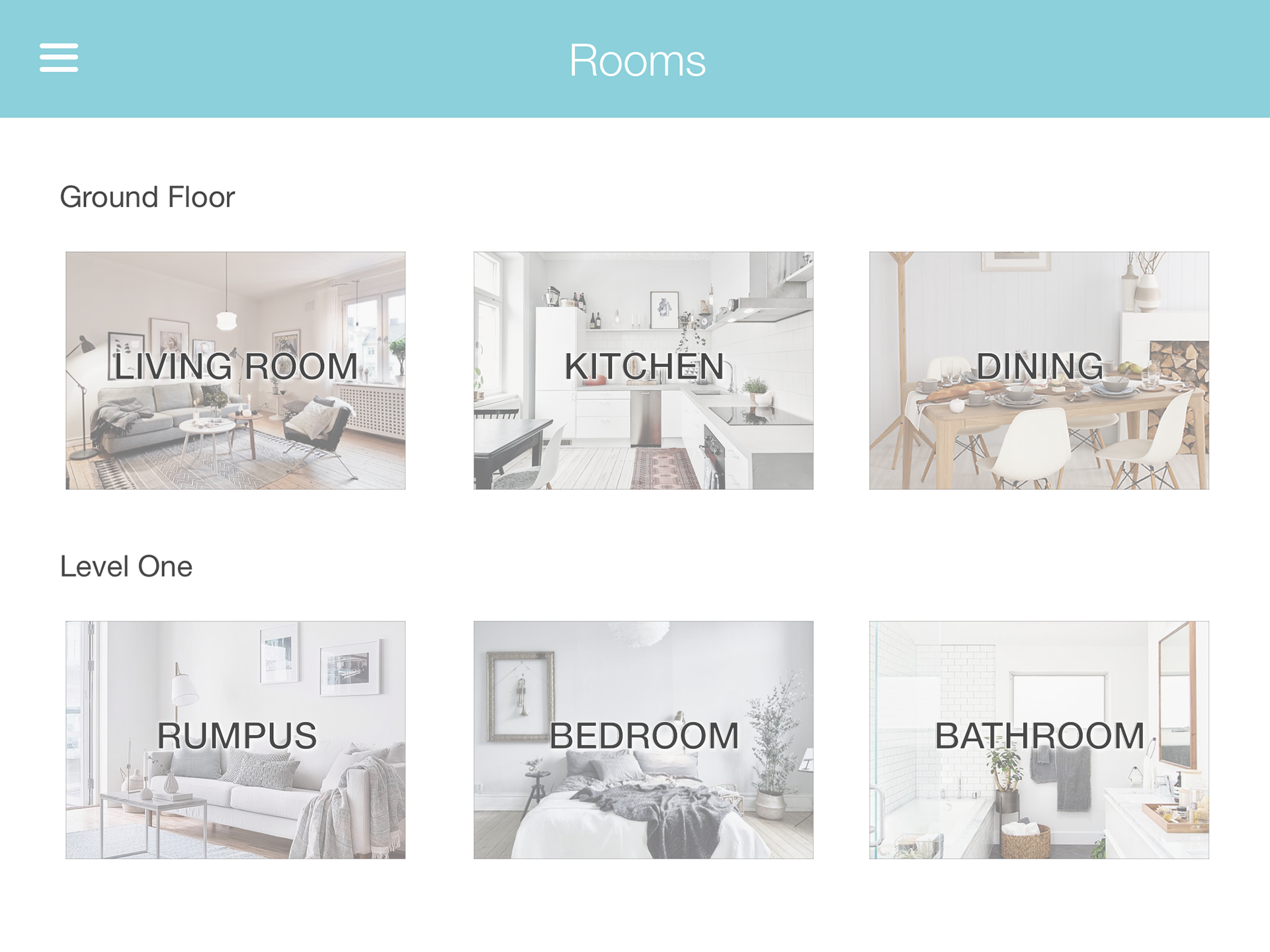
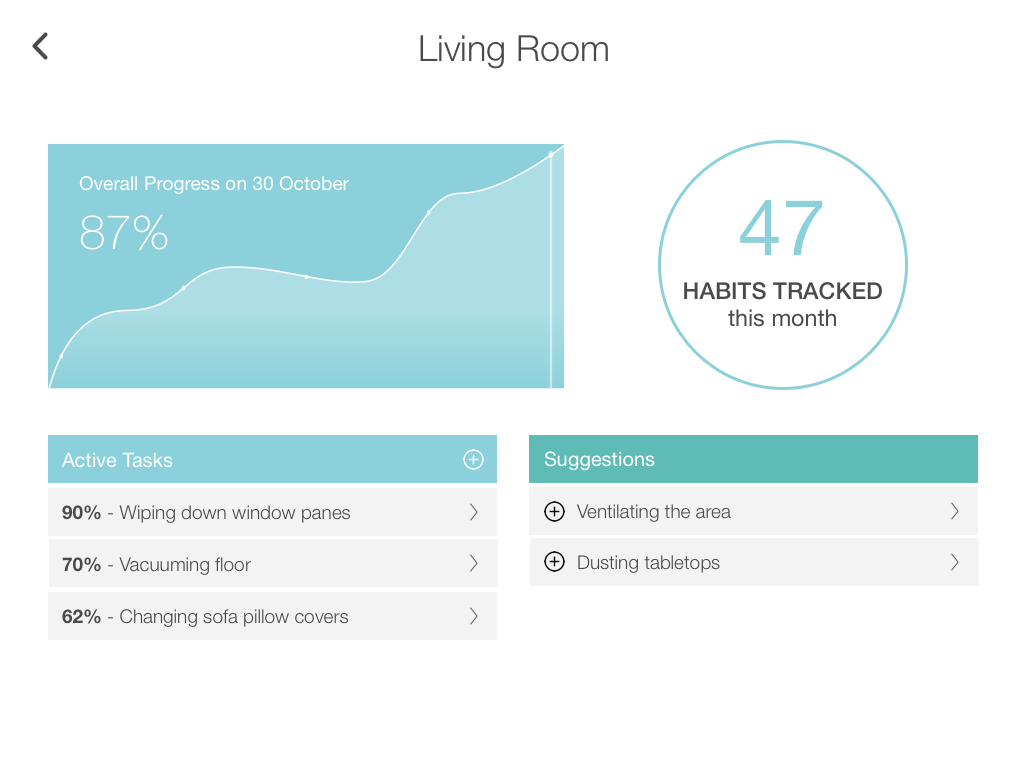
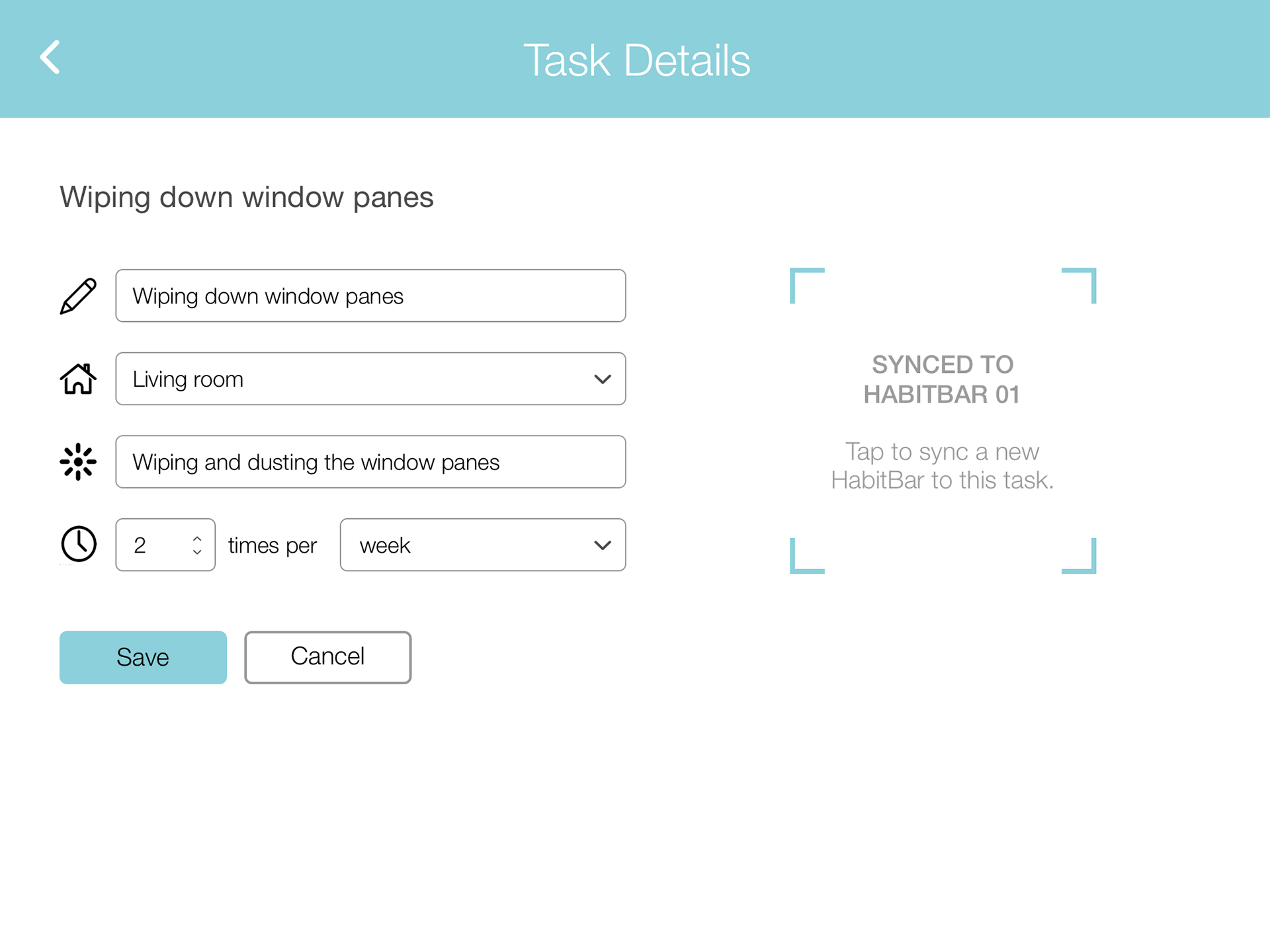
Video Documentary
A comprehensive video was created to thoroughly document our design process and explain how Habitracker works. This video highlights the problem we aim to address, demonstrates our interactive AI solution, and showcases the detailed steps we took from initial research to final implementation. By watching the video, viewers will gain a clear understanding of how our solution responds to the design brief and improves the quality of life for users with atopic disease. The video serves as a testament to our commitment to user-centred design and the innovative application of AI in home healthcare.
Key Takeaways
Throughout this project, several key insights emerged. Conducting user testing with a larger range of potential users, including atopic disease sufferers, would provide more comprehensive feedback and further validate our design. Additionally, further research into atopic disease triggers could enhance the system's support for users and improve prevention measures. Iteratively designing and testing a higher fidelity interface with users is essential to ensure optimal usability and user satisfaction. These takeaways underscore the importance of continuous improvement and user-centred design in developing effective health solutions.
GROUP MEMBERS: Christine Teng, Nina Osada-Phornsiri & Gawshika Aumkaran
Created at the University of Sydney